Fibreglass, a composite material crafted from interwoven glass fibres held together by resin, has garnered significant attention for its unique characteristics. It stands out in industries spanning from construction to aerospace for its strength, resistance to corrosion, and lightweight nature.
This article delves into the origins, defining features, diverse varieties, different applications, and outstanding properties of fibreglass. Keep reading to discover more about this versatile material.
What is fibreglass material?
Fibreglass is a composite material made up of extremely fine glass fibres. These fibres are woven together to form a strong and flexible material. Fibreglass is valued for its strength, durability, and lightweight properties. It is commonly used in a variety of applications including insulation, boat building, automotive components, aircraft, sporting goods, and construction materials. Fibreglass is often chosen over other materials because of its resistance to corrosion, electrical conductivity, and ability to be moulded into complex shapes.
How many types of fibreglass?
There are primarily two types of fibreglass:
- E-Glass Fibreglass: This type of fibreglass is the most common and widely used. It is known for its electrical insulation properties and is often used in applications where electrical conductivity is a concern, such as in electronic components and insulation.
- S-Glass Fibreglass: S-Glass fibreglass is a higher-performance type of fibreglass, known for its superior strength and stiffness compared to E-Glass. It is often used in applications where high strength and durability are required, such as in aerospace components, military equipment, and high-performance sports equipment.
These two types of fibreglass vary in their composition and properties, allowing them to be used in different applications based on specific performance requirements.
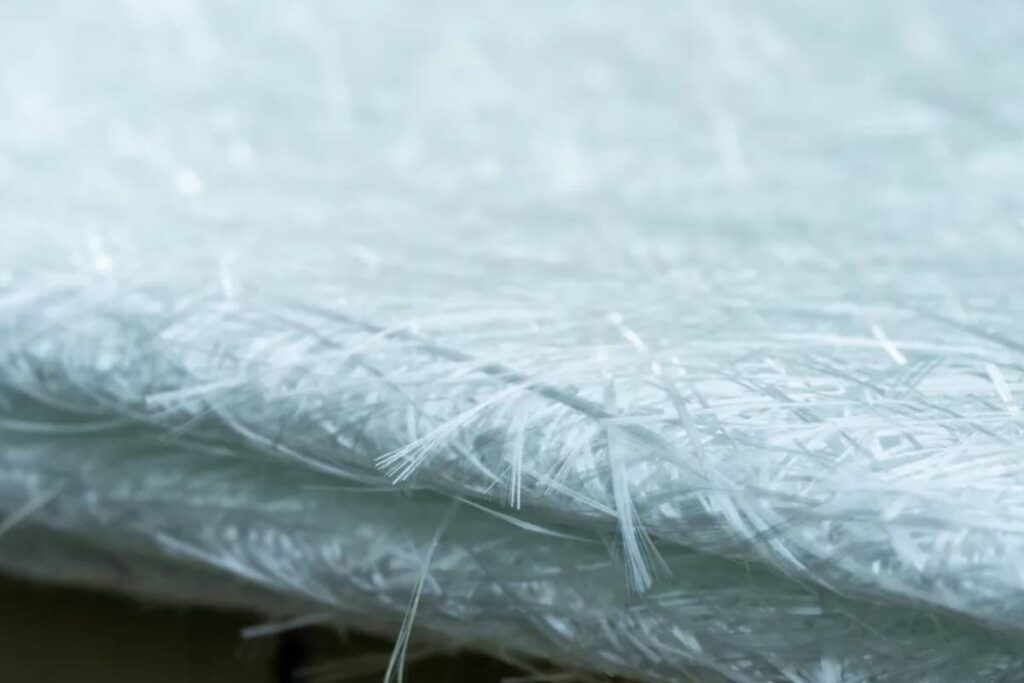

Is fibreglass material safe?
Fibreglass itself is generally considered safe when handled properly. However, like any material, there are potential risks associated with fibreglass if it is not used or handled correctly.
In its solid form, fibreglass is inert and non-toxic. However, when fibreglass is cut, sanded, or otherwise disturbed, it can release small fibres into the air. Breathing in these fibres can irritate the respiratory system and skin, potentially leading to discomfort or allergic reactions in some individuals. Prolonged exposure to fibreglass dust may also cause more serious health issues, such as lung damage.
To minimize health risks when working with fibreglass, it’s important to use proper safety equipment, such as a respirator, gloves, and protective clothing, and to work in a well-ventilated area. Additionally, following safe handling and disposal practices can help mitigate potential health hazards associated with fibreglass materials.
Repeated contact with fibreglass can cause skin inflammation, known as dermatitis, which may trigger allergic reactions. If your fibreglass-related rashes worsen, consult your doctor promptly.
Fibreglass easily transfers from your hands to sensitive areas like the eyes, nose, and throat, posing greater health risks. If you suspect fibreglass exposure in these areas, remove the fibres and seek medical assistance immediately.

Breathing in fibreglass particles while inspecting your skin can cause nasal and throat irritation, coughing, wheezing, breathing difficulties, and nosebleeds, especially for asthma or bronchitis sufferers.
Dry sweeping, inadequate ventilation, and lack of eye protection increase the risk of fibreglass exposure.
If fibreglass dust gets into your eyes, flush them with running water or use an eyewash station for at least 15 minutes. Remove any dust stuck near the eyes by lifting the upper and lower lids.
Even after removing fibreglass, you may experience redness, rash, itching, or discomfort, but long-term effects are rare.
Contrary to popular belief, fibreglass exposure is not linked to cancer or respiratory diseases in humans.
Consult your doctor for guidance on alleviating skin, eye, nose, or throat discomfort after fibreglass exposure.
What is fibreglass used for?
Fibreglass is used in a wide range of applications due to its versatility, strength, and durability. Some common uses of fibreglass include:
- Insulation: Fibreglass is widely used as insulation in homes, buildings, and industrial applications due to its thermal and acoustic insulating properties.
- Boat Building: Fibreglass is a popular material for constructing boat hulls and other marine components because of its lightweight, water-resistant, and corrosion-resistant properties.
- Automotive Parts: Fibreglass is used in the manufacturing of automotive components such as body panels, hoods, spoilers, and bumpers due to its strength-to-weight ratio and ability to be moulded into complex shapes.
- Aircraft Components: Fibreglass is used in the aerospace industry for constructing aircraft components such as fairings, radomes, and interior panels due to its lightweight and high strength.
- Sporting Goods: Fibreglass is used in the production of sporting goods such as fishing rods, archery bows, kayaks, and surfboards due to its flexibility, durability, and resistance to moisture.
- Construction Materials: Fibreglass is used in construction for various applications including roofing, doors, windows, and composite reinforcement for concrete structures due to its strength, weather resistance, and versatility.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: Fibreglass is used in the manufacturing of tanks, pipes, and other equipment for water and wastewater treatment plants due to its corrosion resistance and durability.
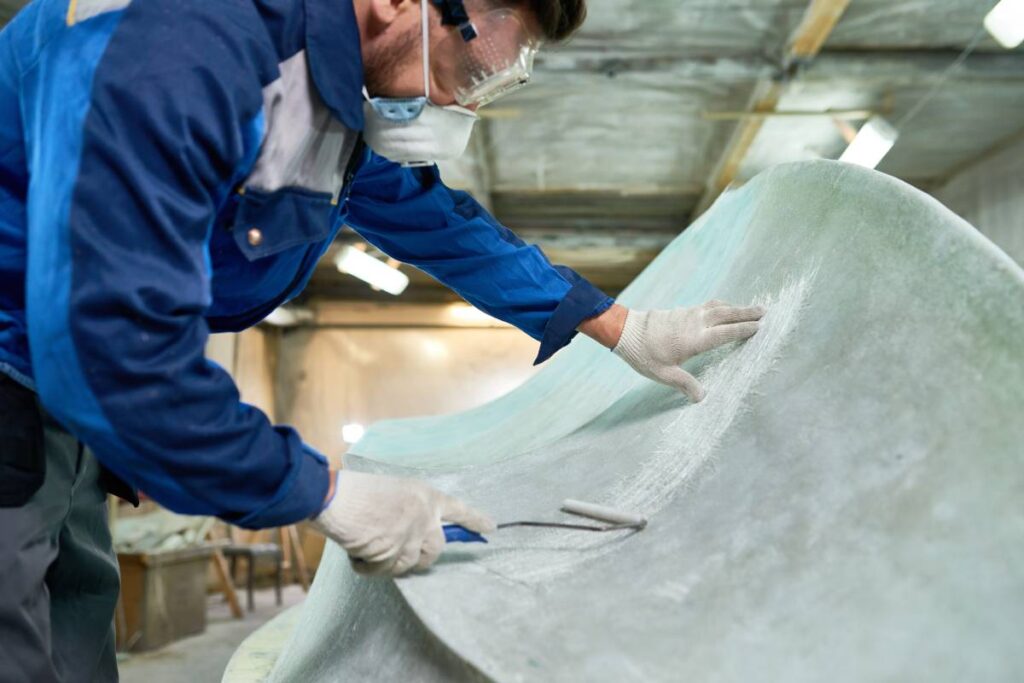

Fibreglass finds widespread application across various industries due to its durability, safety, and excellent thermal insulation properties, making it a preferred material for industrial gaskets. Here’s why fibreglass is extensively used in the following industries:
- Beverage Industry: Fibreglass grating is utilized in bottling lines and brewhouses for its durability and resistance to rust.
- Car Washes: Fibreglass grating is increasingly used for its rust-resistant properties and aesthetic appeal in carwash tunnels.
- Chemical Industry: Fibreglass grating with anti-slip features and chemical resistance is employed in chemical plants, where it is matched with specific resin compounds to withstand the chemicals used.
- Cooling Towers: Fibreglass is used in cooling towers to provide protection from rust and corrosion, ensuring safety in wet environments.
- Docks and Marinas: Fibreglass is used to protect docks from corrosion caused by seawater exposure.
- Food Processing: Fibreglass grating is favoured in food processing plants for its slip resistance and ability to withstand corrosive substances like blood.
- Fountains and Aquariums: Fibreglass supports rocks in fountains and aquariums, protecting spray headers and lights while preventing accidents.
- Manufacturing: Fibreglass grating with embedded grit surface provides slip resistance in wet environments or where oils are present.
- Metals and Mining: Fibreglass grating is used in areas prone to chemical corrosion in electronic refining processes.
- Power Generation: Fibreglass is utilized in tank farms and scrubbers due to its non-conductive properties.
- Plating Plants: Fibreglass grating is chosen for its anti-slip surface in plating plants.
- Pulp and Paper Industry: Fibreglass’s chemical corrosion resistance is valuable in pulp and bleach mills.
- Automotive Industry: Fibreglass is extensively used in automobile components and body kits for its lightweight and durable properties.
- Aerospace & Defense: Fibreglass is employed in manufacturing parts for both military and civilian aerospace applications, including test equipment and enclosures, owing to its strength and versatility.
These are just a few examples of the many uses of fibreglass across various industries. Its properties make it a valuable material for applications where strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion are required.